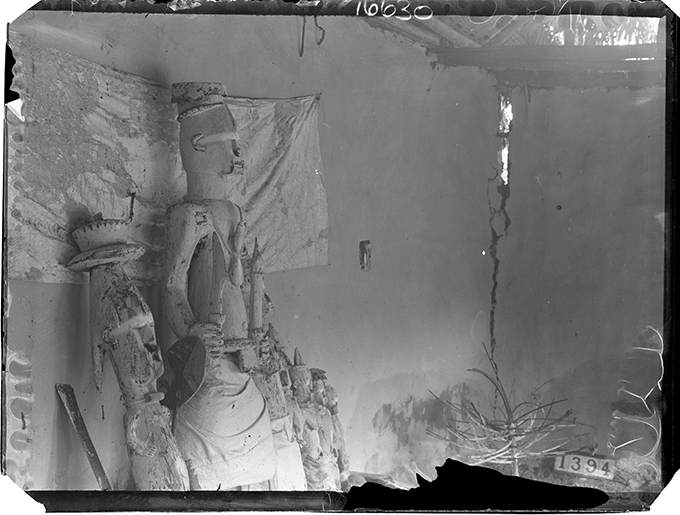
On July 4, 2019 the first of the [Re:]Entanglements project exhibitions resulting from our creative collaborations in Nigeria and Sierra Leone opened at Nosona Studios, Benin City. The exhibition featured the work of 15 young Edo State-based artists responding to the archives and collections that resulted from Northcote Thomas’s 1909-10 anthropological survey of Edo-speaking communities in Southern Nigeria.
The artists had participated in workshops introducing them to the Northcote Thomas materials as well as the work of established artists who have interrogated colonial archives in their practice. Over the past several months they have developed their work, supported by Enotie Ogbebor, Creative Director of Nosona Studios, as well as the [Re:]Entanglements project team.
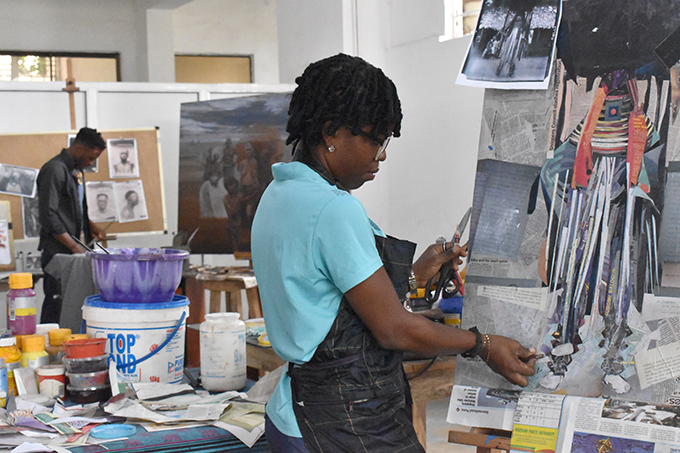
Nosona Studios is a large industrial, workshop type space in the centre of Benin City. In keeping with the character of the space, a section of the exhibition was set up as an artists’ studio, with a number of artists continuing to work on their pieces during the opening. Works included painting; sculpture in wood, bronze and iron; digital art; and mixed media pieces. Each was exhibited with a label illustrating some of the archival source materials that the artists had engaged with. There were also displays of enlarged digital prints of a selection of Northcote Thomas’s photographs, and a TV monitor on which all c.1,800 photographs that Thomas made during his Edo tour played on a continuous loop.
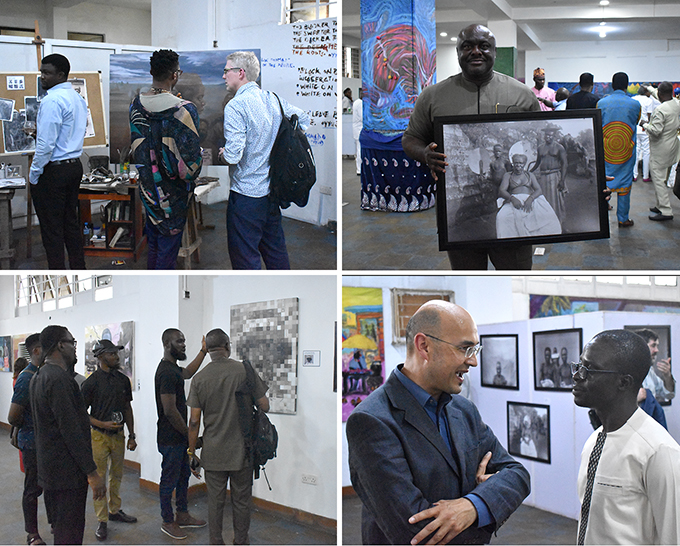

The opening was scheduled to coincide with a meeting of the Benin Dialogue Group in Benin City and served as the venue for the evening reception on the first day of talks. The Benin Dialogue Group is a forum for discussing the future of artefacts looted from Benin City during the British Punitive Expedition of 1897, which are now dispersed in museums and collections across the world. The Group comprises representatives of the Oba of Benin, the Edo State Government, National Commission for Museums and Monuments and several European museums which hold Benin artefacts in their collections. This provided a wonderful opportunity for young artists to meet and talk to both Nigerian and international members of the museum/heritage/culture sector about their work on the project.
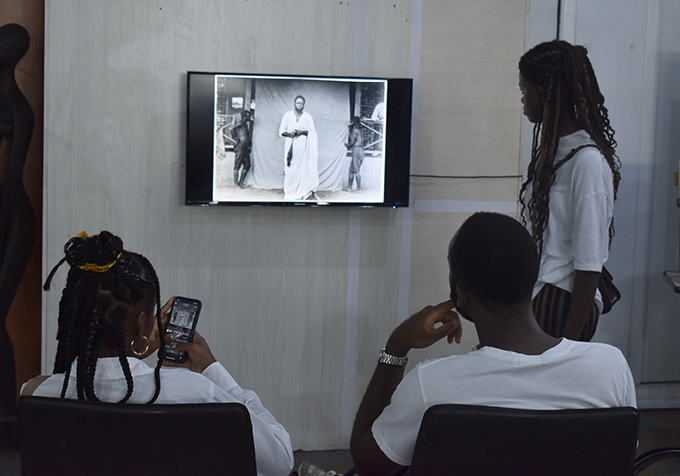


In the following sections, we include a photograph of each of the works produced by the artists and displayed in the exhibition, together with a selection of images providing insight into some of the archival materials the artists worked with in their individual projects. Our commentary is based on interviews with each of the artists. In the case of Enotie Ogbebor and Jahyém Jombo we include the video interviews themselves.
Creative engagements with the colonial archive
Enotie Ogbebor, Chronicles of an Era


Joseph Ogie Obamina, The Anthropological Gaze
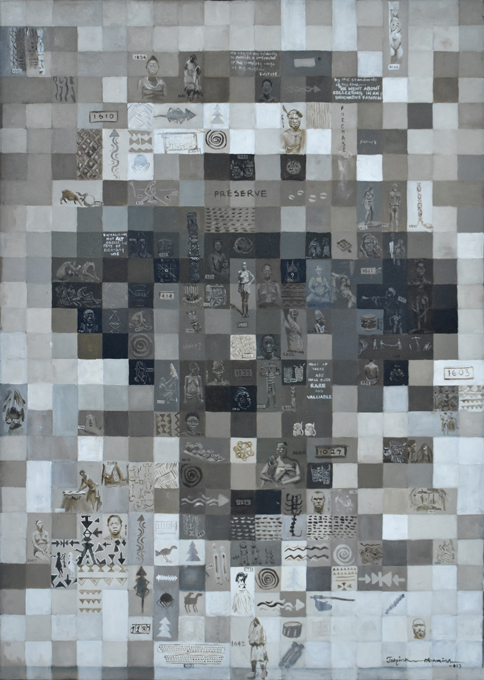


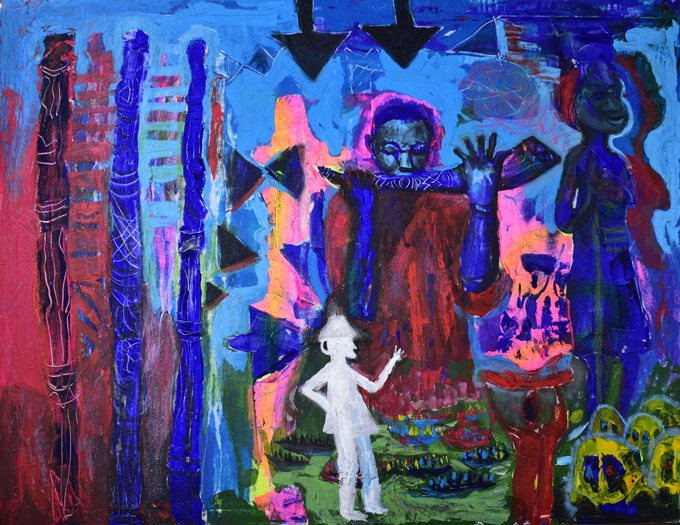
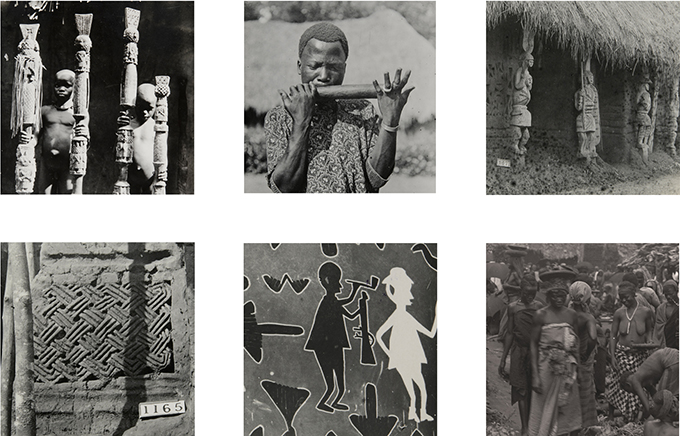
Joseph Ogie Obamina was born in Edo State. He studied art first at Auchi Polytechnic and subsequently at the University of Benin. He works with oil on canvas, and also acrylics and pastel. Obamina was struck by the interchange of gazes evident in Thomas’s photographic archive: the gaze of the people Thomas photographed, and the gaze of Thomas himself through the camera lens. Thomas’s survey of Edo-speaking Nigeria came just 12 years after the Punitive Expedition of 1897. Obamina wonders how they were feeling then – were they oppressed? The photographs show that some were happy, others were not happy. He feels there was some ‘agreement’ between Thomas and the people, which allowed him to photograph almost every aspect of their lives. He is interested in how they perceived the anthropologist.
Obamina expresses this exchange of gazes by creating a pixelated portrait of Northcote Thomas himself, based on the now iconic photograph of the Government Anthropologist wearing his pith helmet, shirt and tie. Viewed from a distance the patterns of the pixels reveal the figure of Thomas. As one approaches one can see that each individual pixel is made up of a scene photographed by Thomas. In addition to reproducing Thomas’s images in the pixels, Obamina adds numbers and texts. The numbers reflect Thomas’s numbering of the photographs, while Obamina uses the texts to add commentary on the nature of Thomas’s anthropological project and its archival legacy.
Ojevwe (Ojay) Onomigbo, Ovia
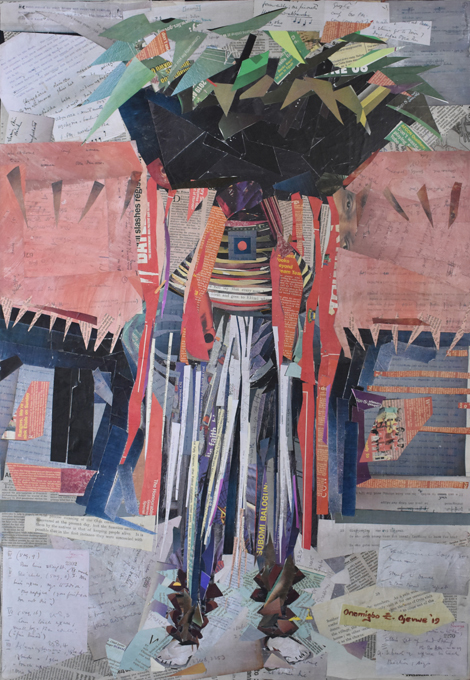


Ojevwe Onomigbo is from Delta State. She is a collagist, who ‘paints with paper’. She studied first at Delta State University and then came to the University of Benin. She has been a practicing artist for about 10 years. Onomigbo created this work, entitled simply ‘Ovia’, during the exhibition’s opening event.
Onomigbo’s work depicts the main masquerade of the Ovia cult at Iyowa. Ovia is a female deity, worshipped in various communities surrounding Benin City. Each Ovia society holds an annual festival at which the ancestral spirits of the society (the masqueraders) dance. Thomas documented the Ovia festival held in Iyowa in 1909. Onomigbo’s reproduction of one of Thomas’s photographs of an Ovia spirit is made from cut up strips and fragments of copies of Thomas’s field notes and publications that document the festival itself.
Jonathan Chambalin Nwachukwu, Game of Numbers
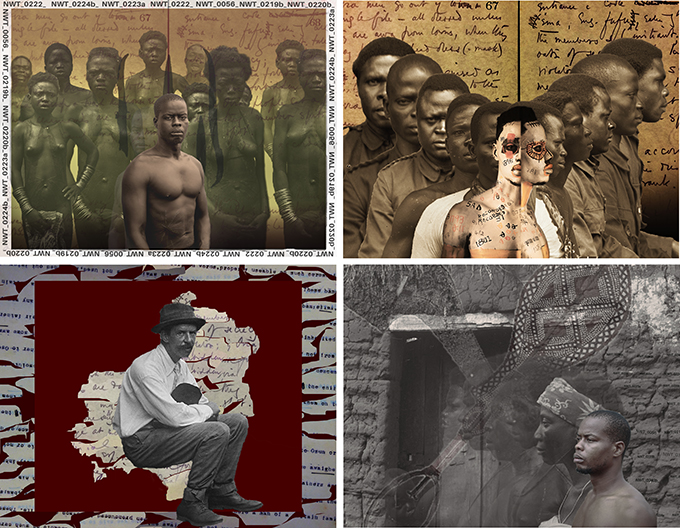


Jonathan Chambalin Nwachuckwu is a photographer and digital artist, working with images and sound. He splits his time between Benin City and Lagos. Like many of the exhibitors, he was first introduced to the archives of Northcote Thomas at a workshop held at Nosona Studios. Nwachuckwu produced a series of six digital animations for the project, which were accompanied by a sound track combining archival and contemporary recordings. His works involved collaborating with a painter, a spoken-word artist, an animator, sound engineer and a number of models.
Each of the six pieces explored a different aspects of the Northcote Thomas archives, from his documentation of female Iwu body scarification to his physical type photographs of members of the local police force. Each work involved the layering of archival images and texts with Nwachuckwu’s contemporary photographs of models posed in the manner of Thomas’s anthropological subjects – their bodies sometimes painted with numbers and symbols. Another digital collage shows a more dejected looking Northcote Thomas himself superimposed on a map of Benin City torn out, as it were, from Thomas’s own notes.
Andrew Omote Edjobeguo, First Contact


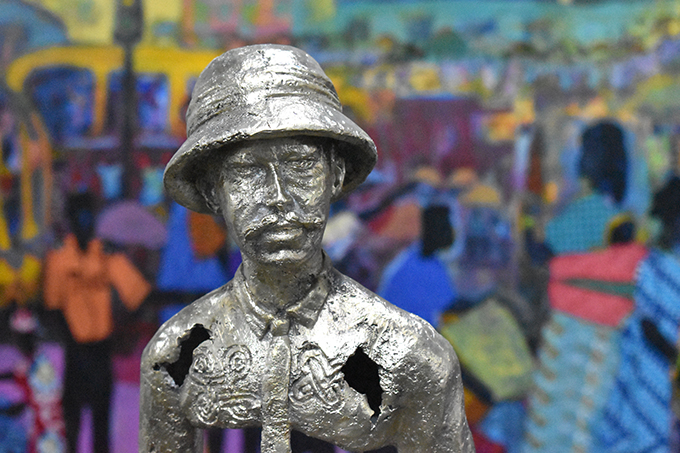
Andrew Omote Edjobeguo is from Delta State. He studies art and industrial design at Auchi Polytechnic. A sculptor, he works in different metals including bronze and mild steel as well as recycled scrap metals.
In his piece ‘First Contact’, Edjobeguo was interested in exploring the points of contact between the anthropologist and the society he was documenting. Thomas’s survey of the Edo-speaking peoples of Nigeria was his first experience of anthropological fieldwork and his first encounter with Africa. Edjobeguo’s sculpture explores how Thomas was in some sense ‘indigenized’ through this experience (he was thought of as an eccentric who had ‘gone native’ by many in the colonial service). This is represented by the incorporation of Edo design motifs on Thomas’s chest and back. These motifs were, of course, drawn from Thomas’s documentary photographs.
The piece also reflects the entanglement of Thomas and Edo culture. Thomas’s career is, as it were, propped up by Edo culture (or a distorted version of it), represented by the ukhure that support Thomas’s bust. Yet the ukhure themselves are supported by Thomas’s work represented in the open book (his Anthropological Report on the Edo-speaking Peoples of Nigeria).
Jahyém Jombo, Against the Odds
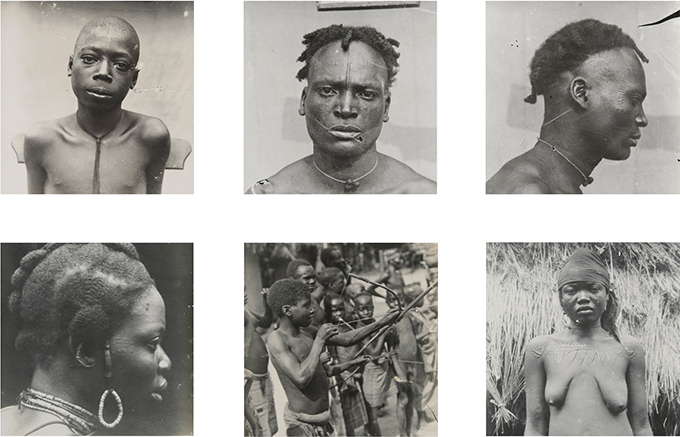


Osaru Obaseki, The Journey amidst Time
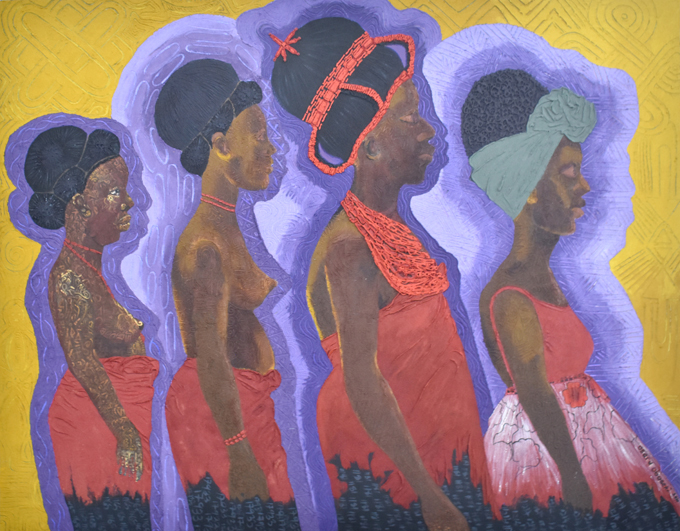


Osaru Obaseki is a self-taught artist from Edo State based at Nosona Studios in Benin City. She paints using a combination of acrylic paint, sand and glue. This adds depth and texture to the surface of her work, into which she inscribes African patterns and symbols. The fine sand she uses also links her work to the ancient bronze casting tradition of Benin – the sand, which is unique to the region, is essential to the lost wax casting technique.
Obaseki was especially interested in the representation of women in Northcote Thomas’s photographs from Benin. In particular she was fascinated by the unnatural, formal poses in which Thomas positioned his photographic subjects. She echoes these group profile portraits in her work for the [Re:]Entanglements project, which is entitled ‘A Journey amidst Time’. Rather than merely reproducing the photographs, however, Obaseki dresses the women differently, showing the continuities and changes in their attire and hair styles over the 110 years since Thomas visited Benin. In the background, she inscribes abstract designs into the acrylic-sand mix, quoting from the designs which decorated the walls of houses that Thomas documented in his Benin photographs.
‘I am so happy that Northcote Thomas was there at the time to document the way women looked, what they did, how they dressed’, Obaseki explains. ‘It was really exciting seeing the photographs – I also saw a picture of my great-grandfather, Chief Agho Obaseki. I was thrilled’. Reflecting on the importance of the archive, she states that ‘it encourages us to do more now to cultivate a culture of documentation for posterity’.
Randy Osabuohien Edughaen, Ol’akohen (The Flute Player)


Randy Osabuohien Edughaen is an artist from Benin City. He studied art at Auchi Polytechnic and the University of Benin, and is now based at Nosona Studios. Edughaen explains how excited he was to participate in the [Re:]Entanglements project and the opportunity to explore the Northcote Thomas archive. ‘This archive is so important to me’, he states. ‘I am the kind of person who doesn’t attach much value to my culture, I don’t know why. But this archive has opened my eyes to my culture. It has made me understand our collective past. Looking at the face of the people in Thomas’s photographs. They have all gone. Their bones must be dust, but seeing the faces of my people gives me joy. Thomas has been able to conserve our culture. He makes me understand where I am coming from. We should try to understand our people – their artefacts, their way of life, their way of dressing … Moving from place to place, Thomas was able to capture these things’.
The dominant figure in Edughaen’s painting, inspired by a photograph taken by Thomas, gives the painting its title, Ol’akohen (‘The Flute Player’). It is the flute player who can communicate with the spirits of the ancestors. The passing of time is the central theme of the piece. Images of the past captured in Thomas’s photographs pass, like sand through an hour glass, through the body of the flute player and are brought up-to-date in colour scenes drawn from press cuttings charting more recent transformations in Benin life, culminating in an image of the present Oba Ewuare II. Among the press cuttings pasted onto the canvas, one in particular poses a challenging question: ‘What Are You Doing About Saving Our Culture?’
Victor Chiejine Mowete, Ọmwan nọr dia uyi ẹdo yi
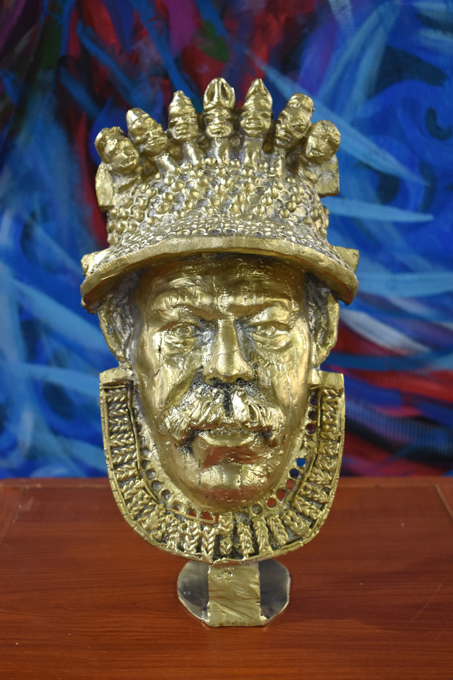
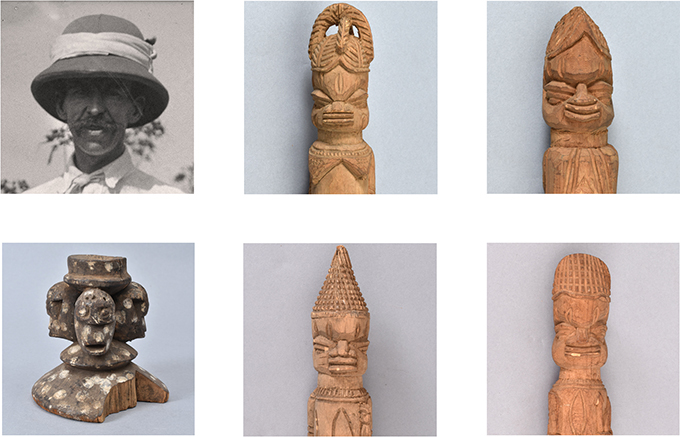


Victor Chiejine Mowete is a sculptor who works in various metals, including steel and bronze. He trained as an artist at Delta State University and the University of Benin. Like many of the artists collaborating with the [Re:]Entanglements project, Mowete is conscious of the ambivalence surrounding the Northcote Thomas archives. He is interested how over time, photographs and collections that were assembled as part of a colonial project – with all its associations with appropriation, exploitation and violence – have become important resources for present-day populations. As he says, ‘Those things that were collected for exploitative reasons, in later years are also going to be important to us and can be used to our own advantage’.
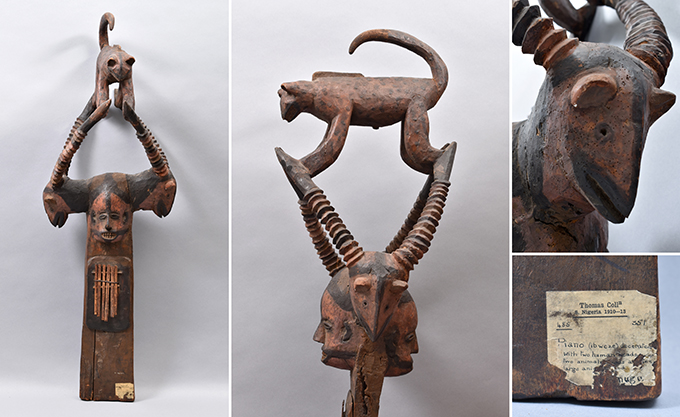
For his contribution to the project, entitled Ọmwan nọr dia uyi ẹdo yi (meaning ‘Preserver of Edo culture and glory’), Mowete has cast a work in bronze that speaks to one of Benin’s most iconic treasures – the 16th-century ivory Idia pendant mask, versions of which are in the collections of the British Museum in London and Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. This famous mask was also used as the emblem of FESTAC in 1977, thus becoming an icon of Nigeria and African arts and culture more generally.

In place of the Iyoba – the Queen Mother, Idia – Mowete has used the head of Northcote Thomas wearing his distinctive pith helmet. The top of the original mask is decorated with heads representing the Portuguese, symbolizing Benin’s alliance with and control over Europeans. These have been replaced, in Mowete’s work, with the heads from various ukhure (rattle staffs) that Thomas collected in Benin City, as well two heads taken from a carved shrine figure (ikute) collected by Thomas from Okpe. Thus, the ambiguity remains: the piece is, on the one hand, a celebration of Thomas as the ‘preserver’ of Edo cultural heritage; on the other hand, however, there is the suggestion that this preservation entails the control of the ancestral objects and knowledges that Thomas assembled as a government anthropologist.
Yewande E. Oyeniyi, Evolution of Benin Attire
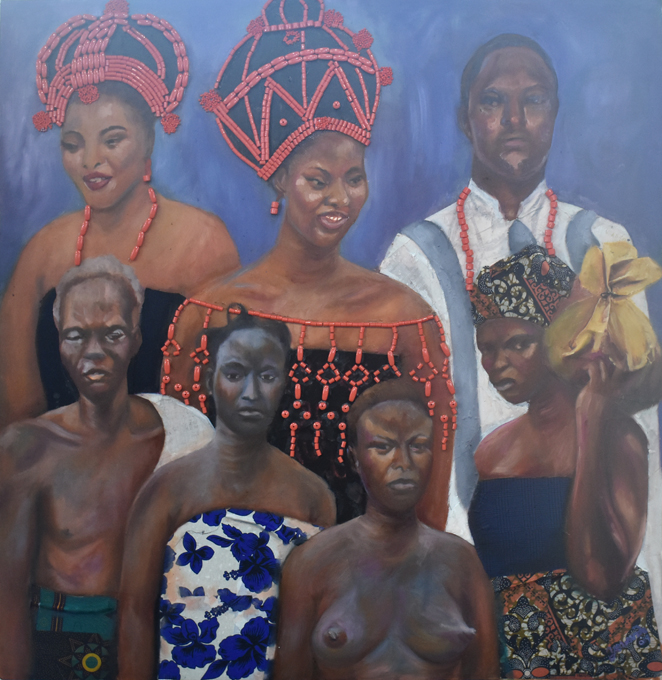


Yewande Oyeniyi initially studied Fine Art at Yaba College of Technology in Lagos, and is now pursuing postgraduate studies in Theatre Arts at the University of Benin. Oyeniyi was particularly interested in representations of women in Northcote Thomas’s photographic archive and chose to focus on dress in her work for the project: ‘Evolution of Benin Attire’.
When Oyeniyi started to engage with the archive, the impression she had was of a timeless world in which there was no anticipation that things would change. Many of the women photographed were unselfconscious of their exposed breasts, for example. Oyeniyi wanted to explore how this had now changed with Western influence that was already apparent in Thomas’s photographs. She also wanted to show how certain aspects of traditional Benin attire, notable the red coral beads, which were once the preserve of the elites, had become more widely popular and iconic of Benin identity.
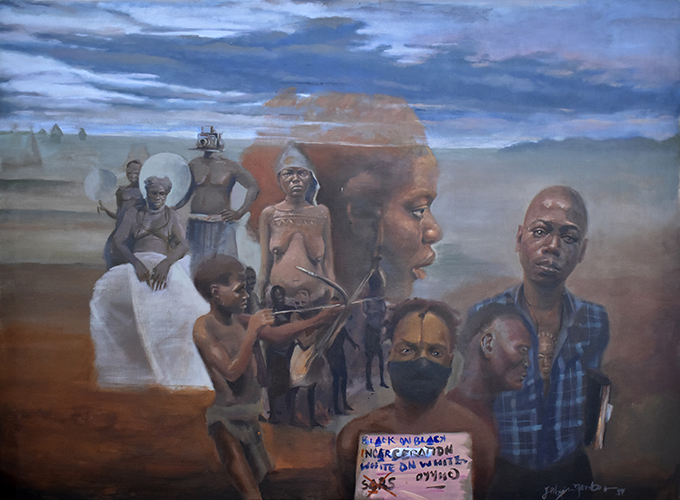
Imoudu Ameen Bello, Loss or Gain?


Imoudu Ameen Bello is from Edo State. He works with oil on canvas. Bello is particularly interested in Benin’s royal heritage and its system of palace and town chiefs. Since Thomas’s survey of Edo-speaking communities took place between 1909-10 when Ovonramwen was in exile in Calabar, the Oba is, of course, conspicuously absent from the archive. Bello was, however, particularly struck by Thomas’s photographic portrait of Chief Ero, Izedonmwen, and his son, Evbuomwan. From ancient times, the Ero chiefs were senior members of the Uzama (king-makers) of Benin. Izedonmwen was a particularly celebrated Ero and was instrumental in the restoration of the monarchy after Ovonramwen’s death in 1914.
Bello created a diptych for the [Re:]Entanglements project, posing a question regarding what was lost and what gained in the encounter between European colonisers and the Edo people. The panel on the left represents a people embedded and inseparable from their indigenous culture. This is represented by the traditional Edo design motifs on both background and the bodies of the people. The panel on the right represents the same scene today. Edo cultural heritage, again represented by the traditional designs, now merely acts as an aesthetic background, while the people – especially the younger generations – go about in Western-styled clothing. Bello states that ‘We are doing away with our own lifestyle, and adopting that of the European’. Despite being part of that colonial contact, Bello is grateful that Thomas came to Benin and documented traditional life.
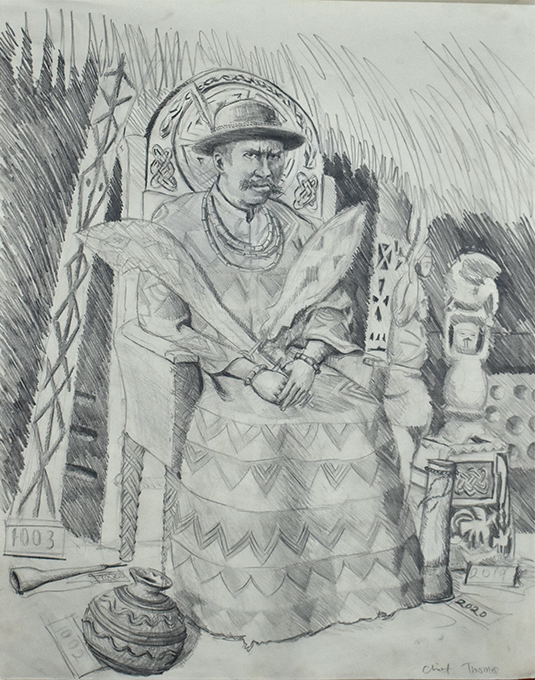
Bello also prepared a preliminary sketch for another work that we hope he will develop entitled ‘Chief Thomas’. It portrays Northcote Thomas as a traditional Benin chief, seated on a throne, and surrounded by artefacts that he collected and documented during his 1909-10 anthropological survey.

O. Kenneth Ugherughe, Glass Plates
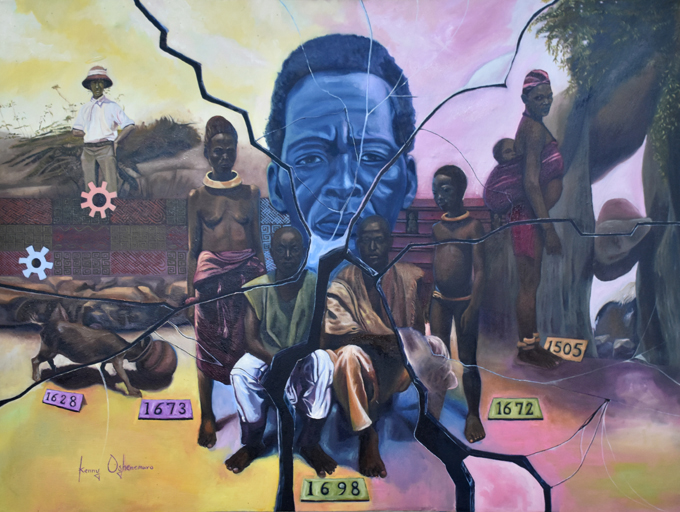
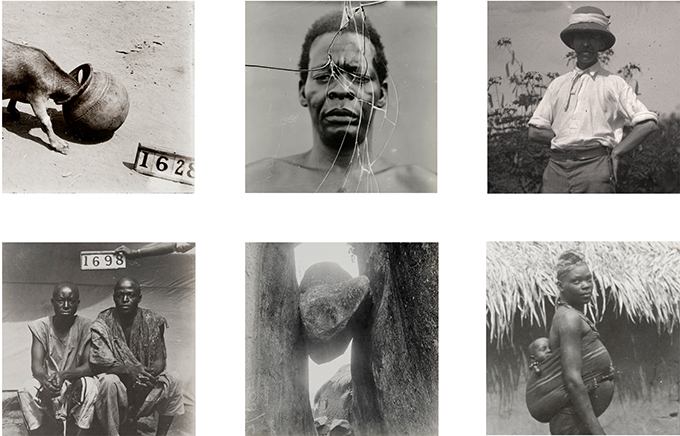


Kenneth Ugherughe was born in Benin City, though his family hail from Delta State. He works in oil on canvas. His work, ‘Glass Plates’, is a reflection on the fragility of the archive. Northcote Thomas’s photographs were exposed on glass plate negatives. A number of these negatives have been broken over time and reassembled by the [Re:]Entanglements team in the process of digitisation. In his painting, Ugherughe pieces together different fragments from the photographic archive in his new composition. Although he insists that he did not intend his painting as a critique of colonialism, we find it hard not to read these broken plates in the light of the fracturing impact of colonialism on Edo society. What was broken in Thomas’s efforts to document traditional Edo life, including its ‘secret societies’ and ritual performances, which were not intended to be accessed by outsiders? Working merely 12 years after the destruction of Benin City at the hands of the British expeditionary force, might it be said that Thomas was documenting a social world that had been irredeemably damaged?
Tony Efeakpokrire, Voices from the Past
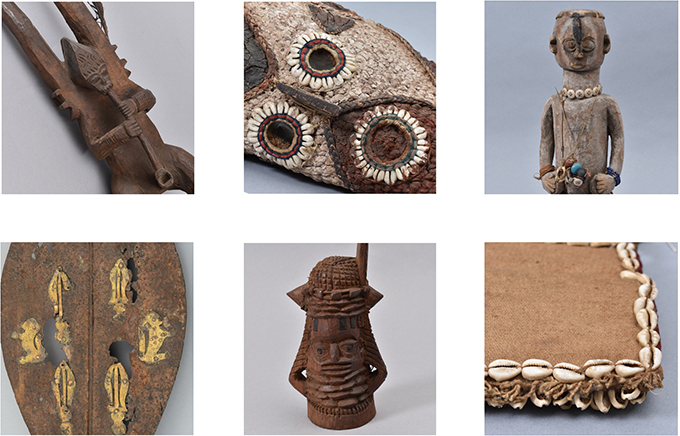


Tony Efeakpokrire was born and bred in Warri, in Delta State. He studied art at Auchi Polytechnic and now works as a studio assistant at Nosona Studios. This give him the opportunity of practicing his art on a full time basis. In addition to contributing an artwork, Efeakpokrire worked very hard, assisting the project team install the [Re:]Entanglements exhibition (thanks Tony!).
When Efeakpokrire began exploring the Northcote Thomas archives, it was the material culture collections – and especially the sculptural pieces – that spoke to him most. Efeakpokrire is a keen student of Edo history and Edo art and he has read widely on the subjects. Seeing photographs of Thomas’s collections made a great impression on him: ‘I have never seen images like this. I realised that this is what I had been reading about’. He reflected on the differences between reading about traditional art and its functions and actually seeing the objects – even photographs of them – themselves. ‘On a normal day’, he explained, ‘I would just get a history book. I would just read – ok, this is what happened. This is how it went. Finish. Close the book. But with the archive, it is like I have been able to travel back to that period’. This gives rise to the title of his work: ‘Voices from the Past’.
Efeakpokrire composition brings together a series of objects that, he says, almost selected themselves. They are all objects collected by Thomas during his survey of Edo-speaking people, and extend the familiar repertoire of Palace art to the material cultures of other groups in the region. He states that Northcote Thomas is, for him, ‘like a deity of sorts, like an ancestor’. Without the archive created through his work he would not be aware of these things.
Efeakpokrire was struck by how advanced Edo society was at the time Thomas documented it, and he sees the archives as issuing a challenge to the present: ‘These images will play a very big role in our lives. They allow us to understand what has changed. How far have we developed? How far have we come? Where do we need to be? Given the distance in time, have we grown? Have we advanced enough? You can see that our ancestors were so civilized. We need to beef up our game. We still need to put in the work. The archive is a challenge. This is the standard. We don’t need to relax’.
Adeyemi Semiu, Rhythm of Thought
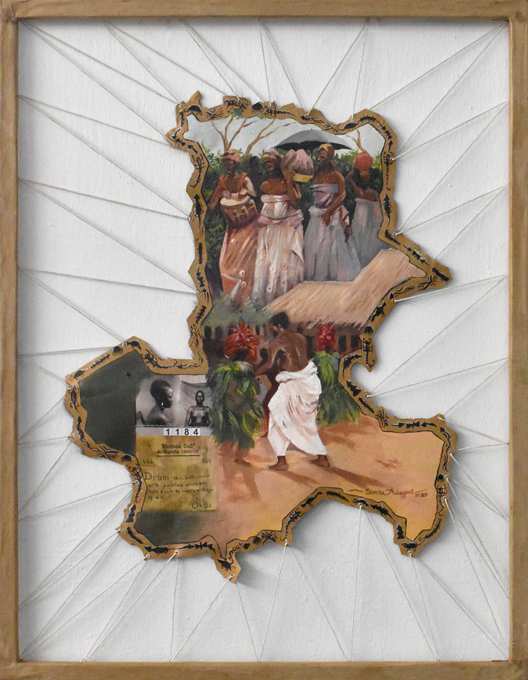
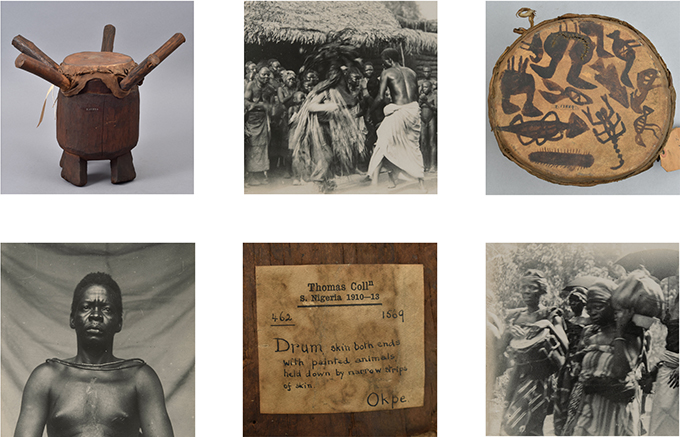


Adeyemi Semiu is an artist based at Nosona Studios working in mixed media. He trained initially at Yaba College of Technology and then at the University of Benin. Semiu was inspired by both photographs and material culture collections in the Northcote Thomas archive. In particular, he was interested in how the archive reflected the more performative aspects of Edo cultural heritage – music, dance, festivals, masquerade.
The music and materiality of the drum are central to Semiu’s work for the project, ‘Rhythm of Thought’. Rather than painting on a stretched canvas, his work is painted onto a stretched animal skin, traditionally used as a drum skin, which he procured from traditional hunters. His medium speaks directly to the drums in the Northcote Thomas collection, including a wonderful example with a painted skin collected in Okpe in North Edo. Semiu uses some of the animal motifs on the Okpe drum to decorate the edge of his work, which is cut and stretched into the shape of the map of the Edo-speaking area of Nigeria published in Thomas’s Anthropological Report.
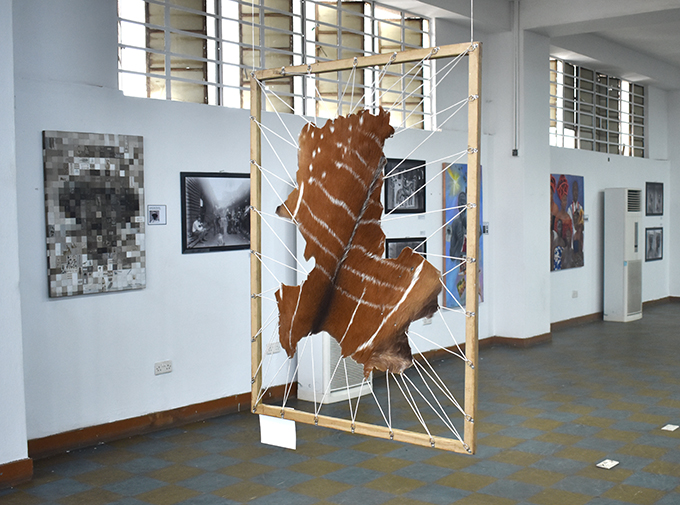

Semiu’s ‘Rhythm of Thought’ is suspended like a mobile from the ceiling in the exhibition, allowing visitors to inspect both sides. Semiu argues that be creating his work on a drum skin, his very medium invokes the memory of Edo’s past.
Ayodeji Ayimoro, The Gods are Safe
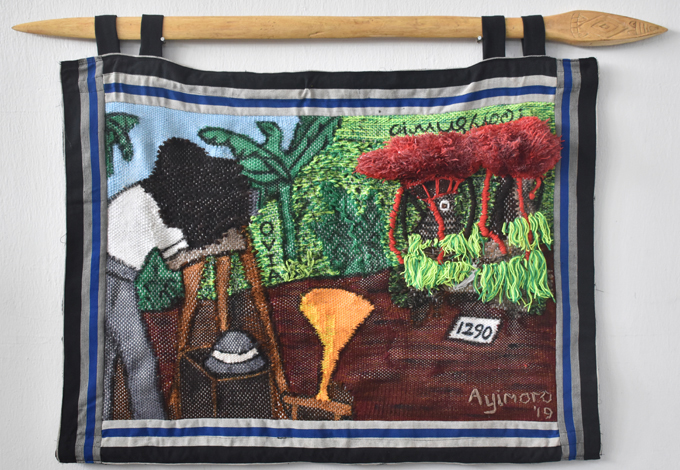
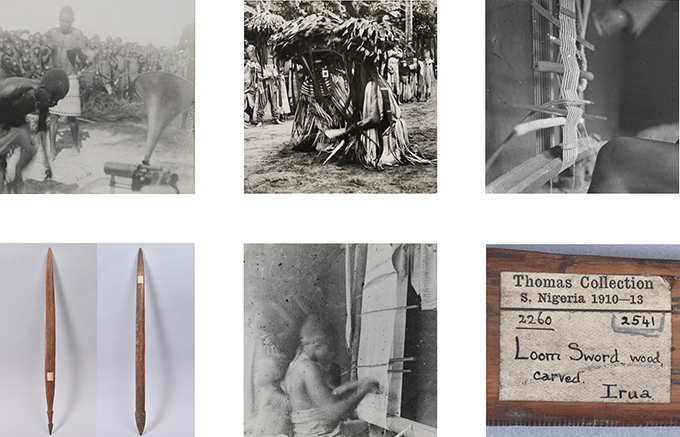


Ayodeji Ayimoro is an artist and textile designer based at Nosona Studios. As someone who works in textiles, Ayimoro was particularly interested in Northcote Thomas’s documentation of traditional weaving in the Edo-speaking world. The work Ayimoro produced for the project is entitled ‘The Gods are Safe’ and it reproduces in a woolen tapestry one of Thomas’s photographs of the Ovia masquerade taken in Iyowa in 1909. The base into which Ayimoro wove his design is piece of cloth he obtained in Somorika, in North Edo, where textiles are still produced using tradition looms as documented by Thomas. The tapestry is suspended on a reproduction of a ‘loom sword’, which were used on traditional looms, to separate the warps and compress the wefts. Thomas collected a number of such loom swords during his Edo tour.
Another interesting apect of Ayimoro’s composition is the inclusion of Northcote Thomas and his equipment. The figure of Thomas is hunched under the dark cloth of his camera in the act of taking the photograph of the Ovia masquerade, while his phonograph machine with its recording horn documents the masquerade song. The process of Thomas’s anthropological survey, including the equipment used and the presence of Thomas himself, is largely absent from the archive, and Ayimoro’s work reinserts this into the frame. Indeed, it is interesting that, in one way or another, most of the artists chose to depict Thomas in their work.
Christopher Osayimwen, Ukhure

The exhibition ‘[Re:]Entanglements: Colonial Archives, Creative Collaborations’ is on at Nosona Studios, Benin City until the end of August 2019. A selection of the artists’ work will later be displayed at the end of project [Re:]Entanglements exhibition at the University of Cambridge Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology.
In addition to the AHRC, the main funder of the [Re:]Entanglements project, we gratefully acknowledge HE Godwin Obaseki and the Government of Edo State for its generous support of the exhibition and opening event. We’d like to thank all the artists who enthusiastically engaged in this creative collaboration with the Northcote Thomas archives, and especially thank Enotie Ogbebor for his enthusiasm and support of the venture. We look forward to many future creative collaborations!






