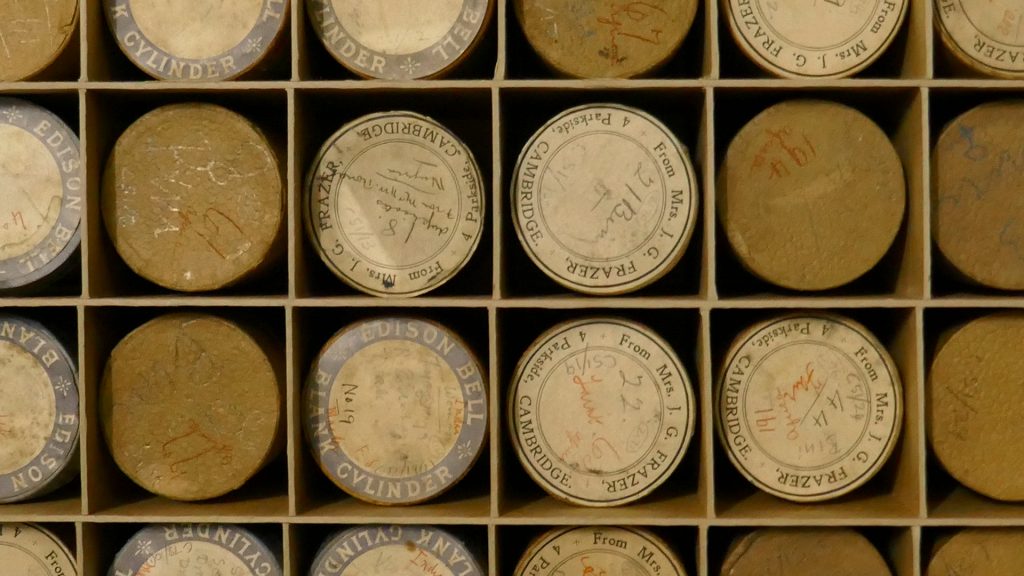
One of the archival legacies of N. W. Thomas‘ anthropological surveys of Southern Nigeria and Sierra Leone is a unique collection of around 750 wax cylinder sound recordings. Since they were recorded using a long-obsolete technology, it had been virtually impossible to listen to the recordings until the British Library Sound Archive digitized them a few years ago. It is only now, however, through the [Re:]Entanglements project that we are beginning to appreciate their remarkable value.
The recordings, which include stories, songs, music, conversations and ‘samples of language‘, constitute an important primary source concerning the histories of the various locations and communities included in Thomas’ itineraries. Due to the poor quality of the recordings and linguistic changes in the areas in which they were made, the recordings are challenging to work with. In an earlier article, Revisiting some Awka folksongs, ethnomusicologist Samson Uchenna Eze discusses some of the difficulties transcribing a selection of the recordings.
As part of our collaboration with colleagues at the University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Dr Ikenna Onwuegbuna of the Department of Music has analysed and reworked a further selection of Thomas’ recordings made in the Igbo-speaking towns of Awka and Agulu in 1911. Onwuegbuna’s grandmother was a well-known singer, and, as an indigene of the Awka region himself, Onwuegbuna is able to provide invaluable insight into the cultural and musical context of the recordings, able to discern nuances and idioms particular to that context. In what follows he provides a kind of masterclass on each of the recordings, before reflecting on their broader significance today.
![Ikenna Onwuegbuna [Re:]Entangled Traditions exhibition University of Nigeria, Nsukka](https://re-entanglements.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Ikenna_Onwuegbuna_Re-entangled_Traditions_exhibition_Nsukka_re-entanglements.net_-1024x576.jpg)
Reworking archival sound
As an ethnomusicologist, music performer and studio producer, Onwuegbuna carefully selected, scrutinized and creatively reworked five of the audio tracks recorded by Thomas. These include three vocal songs, a song performed by a Mmọ̄nwụ̄ (a ‘spirit manifest’ or, less correctly, masquerade), and an instrumental track.
As Onwuegbuna noted in conversation, the limitations of the phonograph sound recording equipment that was available to Thomas are very evident in the recordings. In addition to the high levels of noise, the wax cylinders have an extremely limited dynamic range, and reproduce only a narrow frequency spectrum. The duration of the recordings was limited to about 2½ minutes. Another significant limitation was the fact that recording was made not electronically, through a microphone, but via a horn, which funnelled sound waves onto a membrane upon which a cutting needle was attached. The mouth of the horn had to be placed close to the sound source – thus a soloist singing directly into the horn would produce a good recording, while members of a chorus or instrumentalists positioned further away might not register well.
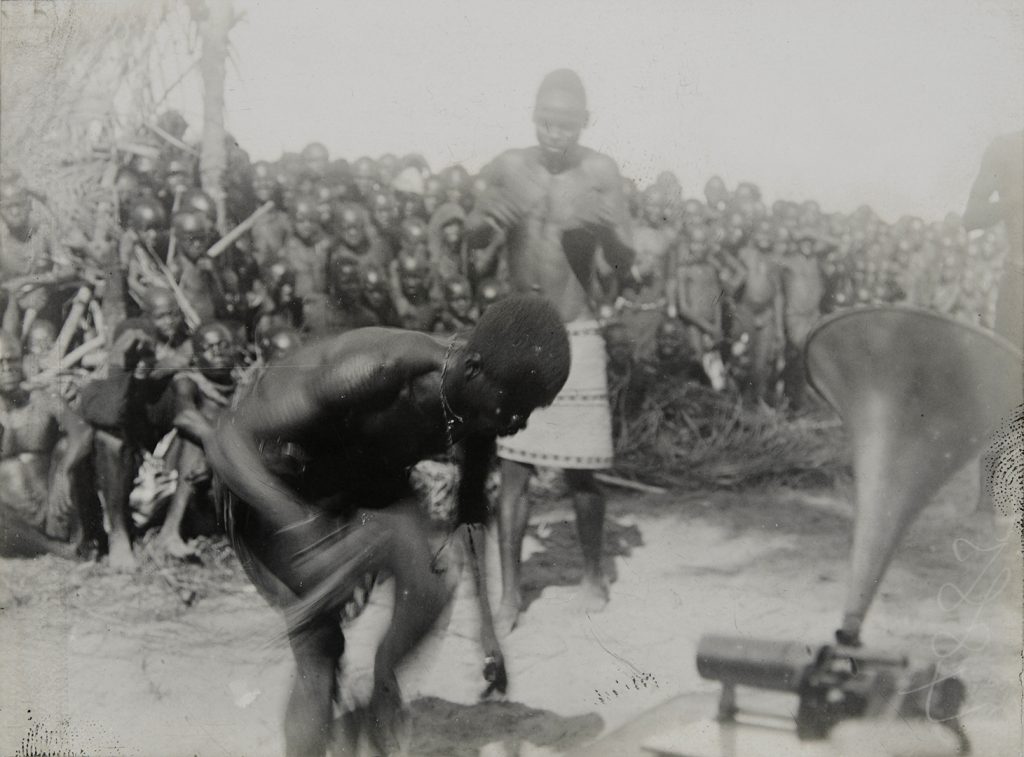
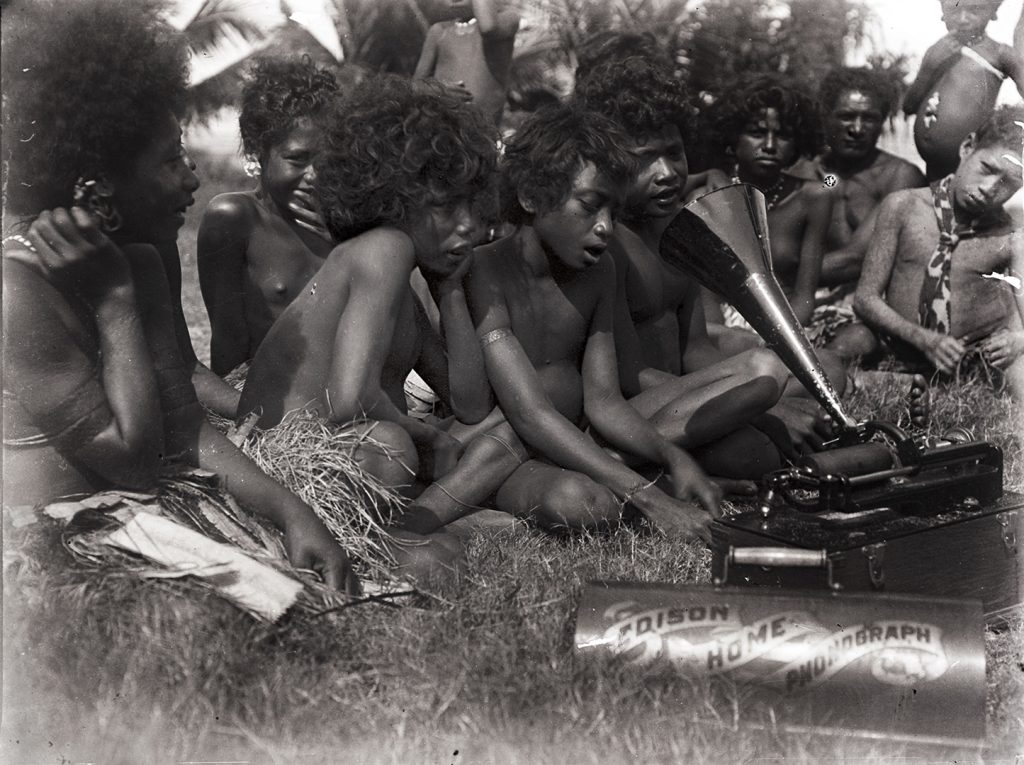


N.34988.ACH2.)
Mindful of these limitations, which convey a distorted impression of this sonic heritage, Onwuegbuna has recorded a new version of each of the historical recordings using modern studio techniques, including sampling of the traditional instruments that would have been used, but which are barely audible in the originals. This has provided an opportunity of imagining how the original performances may have sounded, with a much broader tonal and dynamic range, and complete with choruses and full instrumentation.

For each of the recordings we include the original (digitized) wax cylinder recording made by Thomas, Onwuegbuna’s re-recording of the track, a short video in which Onwuegbuna discusses the original track and how he has reworked it, as well as additional musicological notes.
Kwà-àjáyámmá – vocal group, Agulu, 1911 (#449)
This is a women’s dance song recorded by N. W. Thomas in Agulu, Awka area, in 1911. In reinterpreting the song, I was guided by the thematic contents to supply instrumental accompaniments and vocal harmony to the original. I also enriched the lyrical content by adding some new materials while retaining some of the original contents.
Kwà-àjáyámmá, an onomatopoeic sound and chorused response to the melodic calls of the soloist, is a non-lexical text used in describing the syncopated rhythmic movements of the dancers. As the soloist sings about the innovations that the group has introduced courtesy of their travels to near and far places, this newness is celebrated in chorused response and dance.
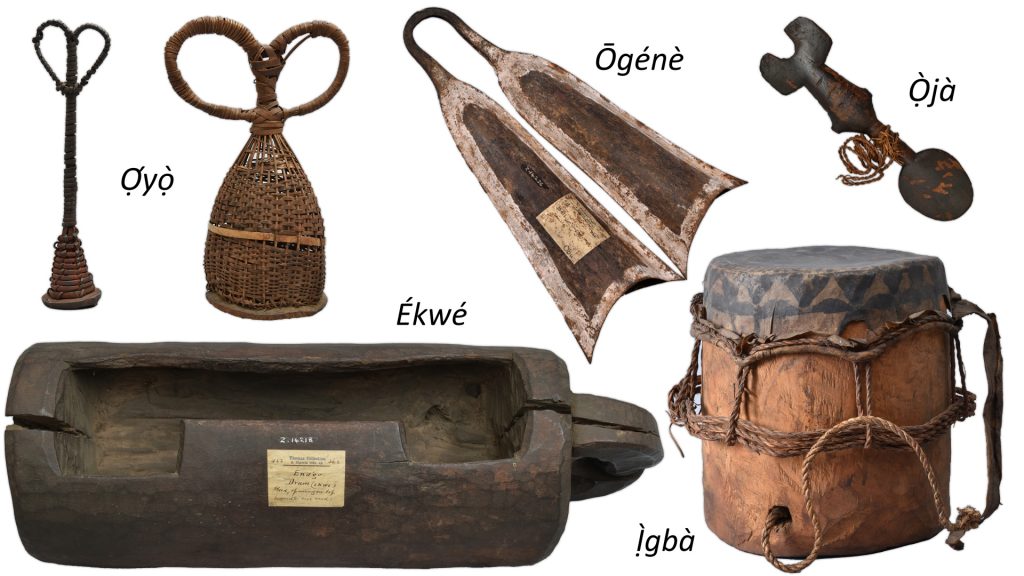
Since Igbo musical instruments have gender inscriptions and gender restrictions, I carefully selected the accompanying instruments along the lines of such bounds.
| Álō (metal gong) | obbligato |
| Ùdù (pot drum) | pulse marker |
| Ị̄chākā (beaded gourd rattles) | rhythmic |
| Ọ́kpọ́kọ́lọ́ (wooden claves) | time referent |
| Ōgénè (clapperless bells) | rhythmic |
| Ékwé (wooden slit-drum) | rhythmic |
Àrụ̀kụ̀ Gbá Ngwā – vocal group, Awka, 1911 (#435)
Àrụ̀kụ̀ gbá ngwā (meaning ‘Àrụ̀kụ̀, hasten up’) was recorded by N. W. Thomas in Awka in 1911, as a female duet. In my reinterpretation, I treated the so-called female duet (which is actually two female voices singing in unison) as a vocal introduction to a mixed-gender dance song. The introduction, in irregular rhythm, is preceded with a horn sound, which warns the listener to expect more in the music than merely a female music ensemble. As the music modulates metrically from irregular to regular rhythm, a dance mode is ignited, accompanied by a dense instrumental texture. This dense texture is further deepened by the vocal harmony of the chorused responses. The lyrics chronicle the history of the group – their collective and individual achievements, and their popularity – and, at the same time, highlights the norms and values of the land. While the onomatopoeic sounds in the chorus are used for exclamations, the chanted words that interject occasionally are declamations – a common practice in a male or mixed gender ensemble.
The instruments deployed in the ensemble include:
| Álō (metal gong) | obbligato |
| Òpù (animal horn) | speech surrogate |
| Ọ̀jà (notched end-blown flute) | instrumental melody |
| Ị̀gbà (membrane drum) | melo-rhythmic |
| Ùdù (pot drum) | pulse marker |
| Ị̄chākā (beaded gourd rattles) | rhythmic |
| Ọ́kpọ́kọ́lọ́ (wooden claves) | time referent |
| Ōgénè (clapperless bells) | rhythmic |
| Ékwé (wooden slit-drum) | rhythmic |
Íyó-ólòlólō – vocal group, Awka, 1911 (#436)
This song, by a vocal group recorded by N. W. Thomas in Awka in 1911, celebrates music, the talent of music-making, and the musicians. In the lyrics, music is metaphorical alluded to as the drum (Ị̀gbà), thereby implying that the group is a mixed ensemble of melodic and rhythmic (melo-rhythmic) instruments. In my reinterpretation, I introduced vocal harmony and instrumental accompaniment.
| Ị̀gbà (membrane drum) | melo-rhythmic |
| Ékpílí (pod rattles) | time referent |
| Ùdù (pot drum) | pulse marker |
| Ị̄chākā (beaded gourd rattles) | rhythmic |
| Ọ́kpọ́kọ́lọ́ (wooden claves) | time referent |
| Ōgénè (clapperless bells) | rhythmic |
| Ékwé (wooden slit-drum) | rhythmic |
Égwú Mmọ̄nwụ̄ – vocal group, Agulu, 1911 (#442)
Égwú mmọ̄nwụ̄ (music of the spirit) captures the reality of the union between the living and the ancestors in Igbo cosmology. Here, two masked singers in muffled voices (ónú mmọ̄nwụ̄) were captured in a vocal performance by N. W. Thomas in 1911 in Agulu. In the call and response vocal interchange, the ‘spirit-manifest’ (Mmọ̄nwụ̄) passes coded information in a simple melody, without any instrumental accompaniment. What I have done, in reinterpretation, is to introduce three instruments while retaining the original vocal melody as recorded by Thomas. In my creative rationalization, a terse texture will still clear the path for the logogenic melody, without masking the message.
The instruments:
| Óké ōgénè mkpị̀ n’ábọ̀ (male twin clapperless bells) | melo-rhythmic |
| Nwúnyè ōgénè mkpị̀ n’ábọ̀ (female twin clapperless bells) | time referent |
| Ọ́yọ̀ (pebble-filled basket rattles) | rhythmic |
Égwú – percussion and flute instrumental, Agulu, 1911 (#448)
In titling this instrumental dance music, I settled for the generic term, Égwú, which not only could translate to music, but also means song, dance, drama, banter, festival, and games. Since it is an instrumental style, I could not think of a better title. As the rhythmic complexity can be felt in a consortium of percussion instruments, the resultant groove provides a soundscape to support and project the emotional dynamics of the melodic instruments. To further deepen the already dense texture of the original recording by Thomas, I introduced a pentatonic-tuned xylophone that occasionally breaks the dominance of the flute melody.
The featured instruments in my edition include:
| Ọ̀jà (notched end-blown flute) | instrumental melody |
| Ngédégwū (xylophone) | instrumental melody |
| Ọ́kwá (double-slab xylophone) | melo-rhythmic |
| Ị̀gbà (membrane drum) | melo-rhythmic |
| Ékpílí (pod rattles) | time referent/rhythmic |
| Ùdù (pot drum) | pulse marker |
| Ị̄chākā (beaded gourd rattles) | rhythmic |
| Ọ́kpọ́kọ́lọ́ (wooden claves) | time referent |
| Ōgénè (clapperless bells) | rhythmic |
| Ékwé (wooden slit-drum) | rhythmic |
| Ọ́yọ̀ (pebble-filled basket rattles) | rhythmic |
| Wooden clappers | rhythmic |
Cultural loss and revival
by Ikenna Onwuegbuna
This ethnomusicological re-engagement with the sound archive has provided an opportunity to peep into the history of the Awka people, with a view to ascertaining the nature and features of their music, including their compositional practices and performance techniques. It enables us to reflect on continuities and changes in the phenomenon of folk artistry.
Reflecting on the historical recordings, it is clear that the only phenomenon that is permanent is change. Igbo society is undergoing rapid changes due to the influence of globalization on its cultural institutions and practices. This is a consequence of the history of European colonialism in the region and especially the incursion of foreign religion that caused a great change from Igbo traditional religion to Christianity.
For a few decades now, there has been growing consciousness of the importance of cultural revival. Against the background of massive loss of cultural heritage, this cultural revivalist movement has been making slow but steady progress. The effort to conserve what can be conserved, to resuscitate what is almost dead, and to change the mentality of the people about their culture is an ongoing process in Nigeria.
In order to rework the historical sound recordings made by Northcote Thomas during his anthropological surveys one must couple a forensic approach to analysing the originals with an in-depth knowledge of the cultural, linguistic and musicological context. Recreating the full sonic experience using modern studio techniques allows us to recover a musical heritage, which the limitations of Thomas’s wax cylinder phonograph could not capture.
This becomes a significant service to the survival of cultural diversity and to the cultural identity of the Igbo people. This is not merely a matter of historical interest. The musical performances that Thomas recorded in the Awka District in 1910-11 are full of inspirational materials that can be adapted by composers of African popular and art music for their original compositions. They provide resource materials for creative artists in humanities, social sciences and beyond. All these could be harnessed for cultural diversity, advancement and socio-economic development.
Thank you Ikenna for your inspirational work with a small selection of Thomas’s recordings, pointing towards the huge potential of the wider collection. Thanks also to British Library Sounds for providing access to the digitized recordings and a small grant to help facilitate this re-engagement work.