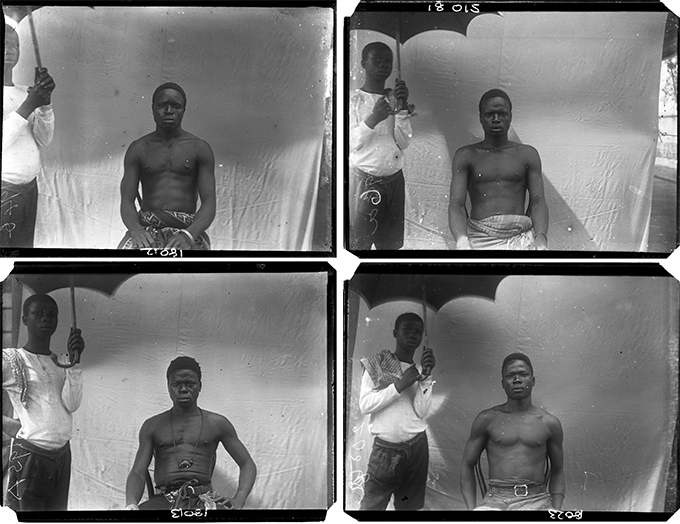
Linguistic research formed an important part of Northcote Thomas‘ anthropological surveys in Southern Nigeria and Sierra Leone. Prior to the early 20th century, most research into West African languages had been undertaken by Christian missionaries. In the context of the emerging colonial sciences, an understanding of local languages was not only useful in terms of communication with local populations, but it also served the project of mapping ‘tribal’ or ‘ethnic’ groups, their territories and their historical relation with one another.
The languages people speak and the tribal or ethnic group names they are given were often used interchangeably. In this respect, Thomas introduced a more nuanced distinction between language and ethnicity. The titles of his published reports therefore refer to the ‘Edo-speaking’ and ‘Igbo-speaking’ people of Southern Nigeria, rather than, for instance, ‘the Edo’ or ‘the Igbo’. Alas, this recognition that language and ethnicity are quite different entities was not reflected in the subtitle of his Sierra Leone report: ‘The Timne and Other Tribes’.
Collecting specimens of language
Methodologically, Thomas’s anthropological surveys in West Africa between 1909 and 1915 were defined by practices of collecting and documentation. Thus, he collected ‘specimens’ of language in much the same way as he collected ‘specimens’ of material culture or, indeed, specimens of local botanical species. The use of the term ‘specimen’ carries an implicit assertion about the ‘scientific’ status of the anthropological surveys and the knowledge they produced, with its connotations of objectivity, rigour and authority. (Qualities that can, of course, all be contested.)
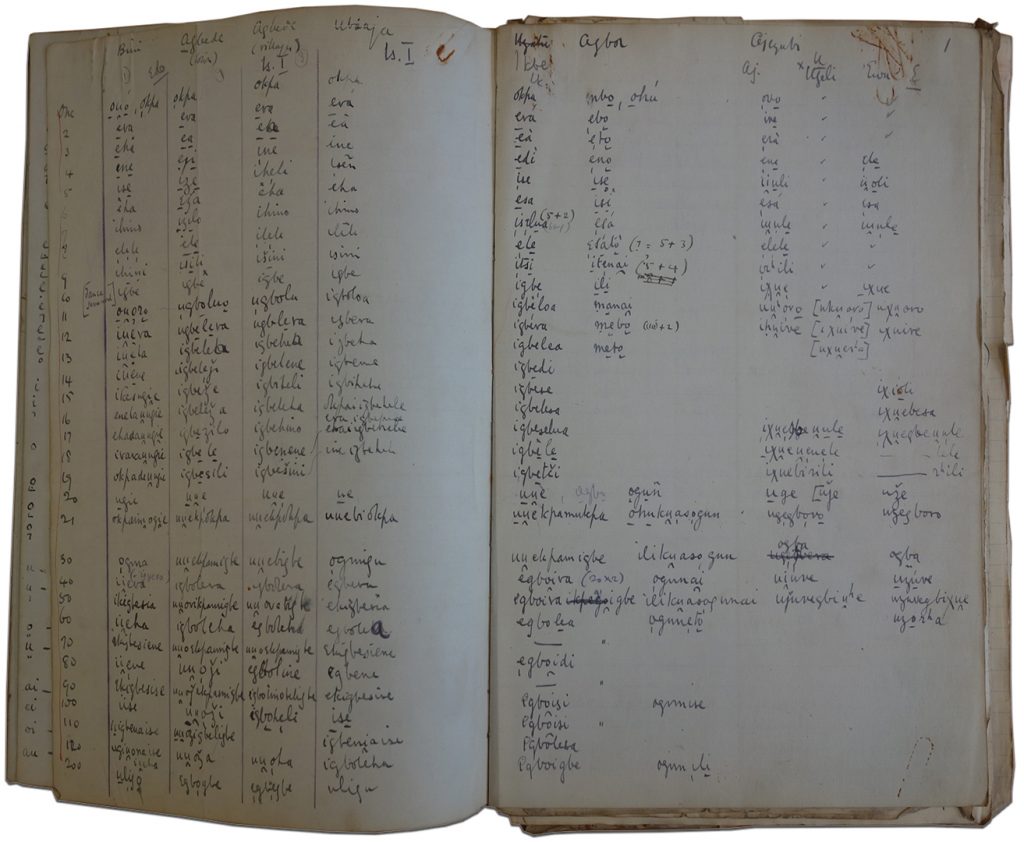
The process of collecting linguistic specimens included the compilation of word lists, phrases and stories. For this, Thomas enlisted the assistance of interpreters. Finding reliable interpreters was a considerable challenge and there is much correspondence on this issue in the Colonial Office archives, especially relating to Thomas’s initial tour as Government Anthropologist in 1909-10. We learn, for example, that Thomas regarded the first interpreter who had been assigned to him – a schoolteacher named Erumese – as ‘reckless and inaccurate’, while he was frustrated that his replacement – a Corporal Nimahan of the Police Force, who was ‘thoroughly competent’ – was obliged to return to his police duties after a period of four months.

Thomas named these interpreters and acknowledged the extent and importance of their contributions in his Edo report. Unfortunately, in his subsequent reports, individual assistants are not named, though there is no doubt that their contributions remained vital. The role of interpreters also went beyond providing linguistic assistance. In a letter sent in 1911, during his second tour in what was then Awka District, for instance, Thomas praised his ‘junior interpreter’, one Alfred Nwile, remarking that he has displayed ‘great intelligence and skill’ in collecting botanical specimens.
The actual ‘collecting’ of words, phrases and stories, whether by Thomas or his assistants, was done either through direct transcription into text or with the use of a wax cylinder phonograph recorder. In appendices to his Edo Report, Thomas provided guidance notes for colonial officials, including use of the phonograph in linguistic documentation, and advice regarding language transcription. He provided a list of 150 words and phrases for translation to allow for comparison across languages, as well as more detailed questions about language usage. These were effectively the same techniques that Thomas and his assistants used during the four anthropological surveys.

Recordings and transcriptions
Thomas wrote up and published the results of the linguistic research from the surveys in various books and articles. These included volumes of his main anthropological reports dedicated to ‘linguistics’, ‘vocabularies’, ‘grammar’, ‘tones’ and ‘dictionaries’, as well as separate volumes entitled Specimens of Language from Southern Nigeria (1914) and Specimens of Language from Sierra Leone (1916), which comprise of pages of tables of words translated into different local languages and dialects. These works were distributed to members of the colonial service, as well as to university libraries. How many people actually read them at the time is unknown – one suspects not many!

Duplicates of the wax cylinder sound recordings were also made available at the Horniman Museum in South London and the Pitt Rivers Museum in Oxford for scholarly consultation. Again, these seem to have been little used. The recordings have now been digitized by the British Library and we have been working with these throughout the [Re:]Entanglements project. In particular, we have been taking the recordings back to the communities in which they were recorded over 110 years ago, and it has been wonderful to witness as people listen to the voices of their ancestors and reconnect with this aural heritage.
In many cases, Thomas published transcriptions of the audio recordings, and it is fascinating to reunite these sounds and texts.
Experimenting with tones
Edo, Igbo and Temne are all tonal languages, in which lexical or grammatical meaning is altered by the pitch contour in which words are spoken. Thomas’s anthropological surveys took place at a time when the science of phonetics was becoming established in universities in Europe. Thomas was a friend of the phonetician Daniel Jones, who ran the Experimental Phonetics Laboratory at University College London. Jones had developed a method for determining what he termed phonetic ‘intonation curves‘ using phonograph cylinder recordings. Jones and Thomas worked together applying this technique to document the tonal changes in the specimens of Igbo speech that Thomas and his assistants had recorded during his 1910-11 and 1912-13 tours. According to Jones’ biographers, Beverly Collins and Inger Mees (1999), this was a pioneering piece of research on tone languages.
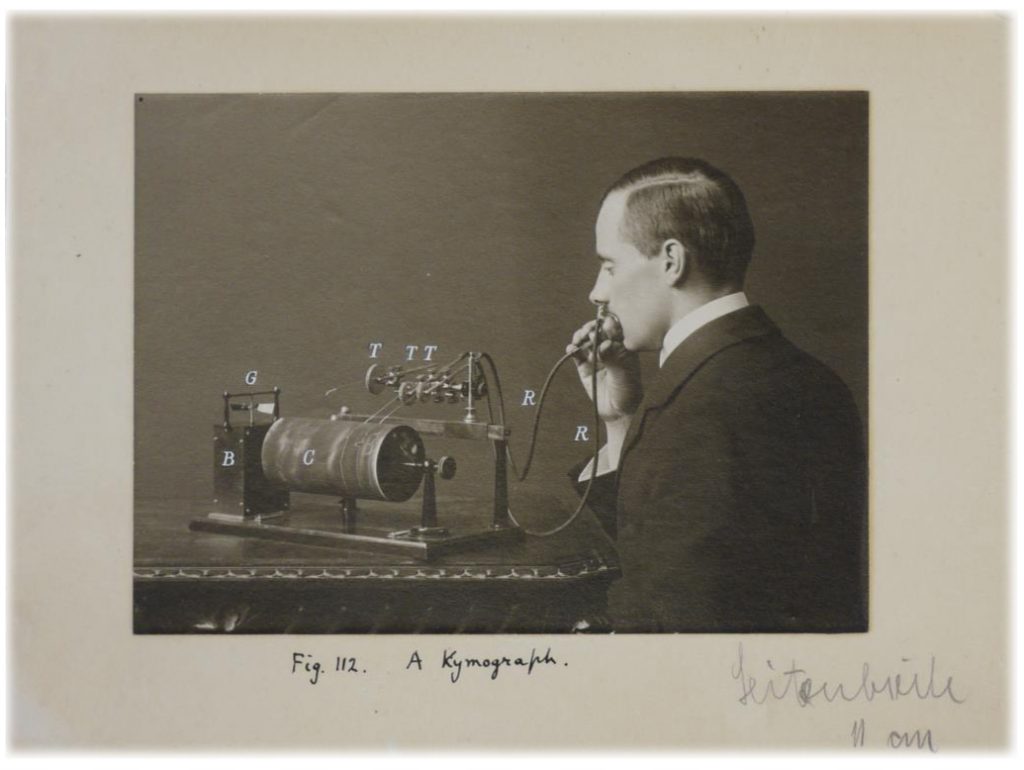

Thomas wrote up the experiment in Part VI of his Anthropological Report on the Ibo-speaking Peoples of Nigeria, providing transcriptions with musical annotations for some of the recordings they worked with. The specimens of Igbo language they worked with include such memorable expressions as ‘Does the goat frighten the dancer?’, ‘He took an egg, cried for a cloth, passed the bridge’ and ‘He put his foot on her waist and caused a big palaver’!


Orthographic debates
In his guidance for colonial officers, Thomas wrote that ‘For the collection of Vocabularies or native texts, two things are essential, one is, a certain amount of training of the ear, the other is an adequate system of transcription’. With regard to this system of transcription, he added, ‘the cardinal principles are, that each sound should have a sign peculiar to itself and that each sign should represent one and only one sound’.
At the time of Thomas’s surveys, there were a number of competing phonetic alphabets in use. Thomas used a system based on modifications to Latin script through diacritical marks. This was based on a Standard Alphabet devised by Karl Richard Lepsius for ‘reducing unwritten languages and foreign graphic systems to a uniform orthography in European letters’, published in the 1860s and recommended for adoption by the Church Missionary Society.
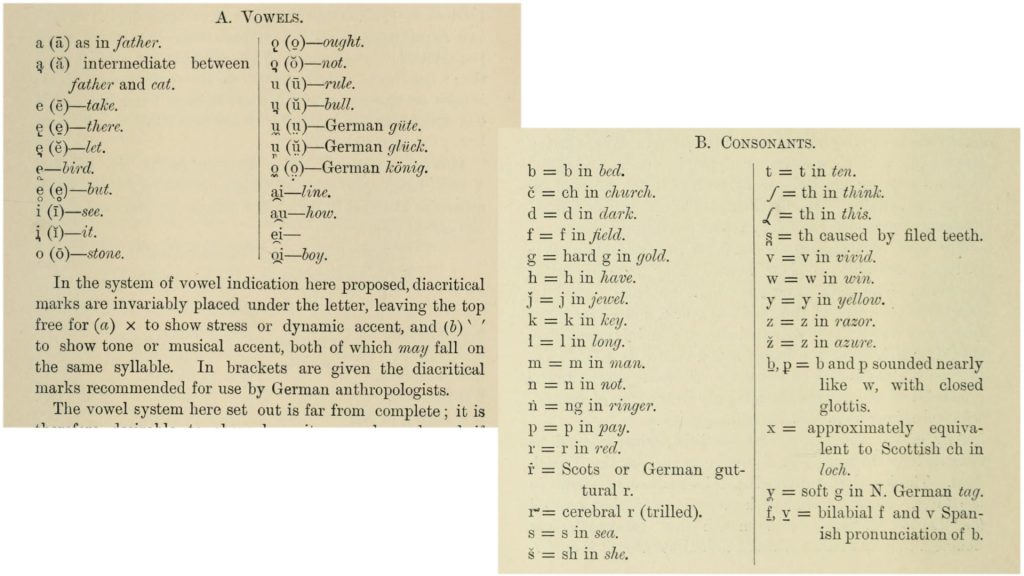
In a review of Thomas’s Anthropological Report on Sierra Leone published in the Times Literary Supplement published in 1916, the reviewer criticized Thomas’s use of ‘inverted vowels and coined accents’, which he found confusing and wondered if there were not a more simple system. This provoked a lengthy exchange in the letters pages of the TLS that lasted seven months, in which numerous authorities debated various issues concerning phonetic spelling.
In Nigeria, the Lepsius system was superseded, first, by the adoption of a ‘Practical Orthography of African Languages’, developed by the International Institute of African Languages and Cultures in the 1920s, and, subsequently – in the case of Igbo – by the Ọnwụ system in the 1960s. The Ọnwụ system consists of 28 consonants and 8 vowel sounds.

N. W. Thomas, linguist?
As may be discerned in the discussion above, Thomas was as much a linguist as he was an anthropologist. In 1914, while he was working in Sierra Leone, he was asked to advise on the introduction of linguistics in the training of new Colonial Service staff. Candidates who passed the examination were entitled to salary supplement. In the National Archives in Sierra Leone we discovered a draft paper Thomas had prepared entitled ‘Elementary Sketch of Phonetics’, which was evidently intended as a introductory text for teaching purposes.

In the event, it appears that this text was not adopted, and George Noel-Armfield’s book, General Phonetics for Missionaries and Students of Languages (1915) was used alongside reprints of the linguistic appendix to Thomas’s earlier Edo report. The latter was used as a guide for candidates who were expected to collect specimens of language from the colonial territories in which they served.
Thomas’s career as a government anthropologist came to an abrupt end in 1915 at end of his Sierra Leonean tour. He did, however, continue to write articles on linguistic themes, including a broader survey of what were then called ‘Sudanic languages‘ (languages of the Sahel belt) published in the Bulletin of the newly established School of Oriental Studies in 1920, and an attempt at reconstructing historical population movements through linguistic analysis in a paper entitled ‘Who were the Manes?‘ published the same year in the Journal of the Royal African Society.
Thomas also taught African languages, as an occasional lecturer at the Imperial Institute in London’s South Kensington, as part of the Tropical African Services Course. Candidates were evidently required to collect and transcribe language samples, as evidenced in a letter we discovered from Llewellyn Travers Chubb, sent to Thomas in 1925 from Bende in present-day Abia State.

Nothing of significance?
What are we to make of all this endeavour today? More recent linguists have been quick to dismiss the value of Thomas’s work. Betram Okolo, a linguist based at the University of Benin, Nigeria, argues that ‘nothing of significance’ was written on Igbo linguistics between 1890 and 1930, and describes Thomas’ efforts as ‘grossly inadequate’ and ‘misleading’. However, his remark that Thomas’ work ‘represents one of the most idle performances offered to the public on the Igbo language’ seems somewhat unfair. Indeed, it seems Okolo was not aware that the records on which Thomas conducted his tonal experiments were also recorded by him and his assistants over six years of fieldwork using primitive equipment in challenging conditions, or just how pioneering were his attempts with Daniel Jones at documenting tonal languages using ‘scientific’ methods.

While we might contest the assertion that Thomas’s linguistic work was an ‘idle performance’, its entanglement in the colonial project cannot, of course, be denied. Joseph Errington argues that ‘Colonial linguistics needs to be framed … as a nexus of technology (literacy), reason, and faith and as a project of multiple conversion: of pagan to Christian, of speech to writing, and of the alien to the comprehensible’ (Errington 2001: 21).
Furthermore, as Judith Irvine has recently noted, ‘These early projects contributed to the shape of African linguistics as we inherit it today, and – as part of the colonial enterprise – they had effects on the lives of the African languages’ speakers’ (Irvine 2008: 324). This is perhaps most evident in the use of (modified) European scripts to render many of Nigeria’s and Sierra Leone’s languages, and in the use of English as their national languages, such that younger people especially are turning away from their local languages.
Revisiting Thomas’s linguistic research
As part of the [Re:]Entanglements project, we have been collaborating with colleagues in the Department of Linguistics and Nigerian Languages at the University of Nigeria, Nsukka. In a future article, linguists Gloria Tochukwu Okeke and Ogechukwu Miracle Uzoagba will report on their experimental research on dialect change, comparing Northcote Thomas’s historical sound recordings with recreations of the same texts by present-day speakers of the same dialect. Their fascinating work suggests that the value of Thomas’s recordings may lie in the future rather than in the past.
Selected references
- Collins, B. and I. M. Mees (1999) The Real Professor Higgins: The Life and Career of Daniel Jones. Berlin & New York.
- Errington, J. (2001) ‘Colonial Linguistics’, Annual Review of Anthropology 30: 19-39.
- Irvine, J. T. (2008) ‘Subjected Words: African Linguistics and the Colonial Encounter’, Language & Communication 28: 323-343.
- Okolo, B. A. (1981) ‘The History of Nigerian Linguistics: A Preliminary Survey’, Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics 6: 99-125.



